K-function
khat.RdCalculates an estimate of the K-function
Arguments
- pts
A points data set
- poly
A polygon containing the points - must be a perimeter ring of points
- s
A vector of distances at which to calculate the K function
- newstyle
if TRUE, the function returns a khat object
- checkpoly
if TRUE compare polygon area and polygon bounding box and convex hull areas to see whether the polygon object is malformed; may be set to FALSE if the polygon is known to be a ring of points
- x
a
khatobject- ...
other arguments passed to plot and print functions
Value
If newstyle is FALSE,
a vector like s containing the value of K at the points in s.
else a khat object list with:
- khat
the value of K at the points in
s- counts
integer matrix of counts of points within the vector of distances
sfor each point- khats
matrix of values of K within the vector of distances
sfor each point- s
s
Details
The K function is defined as the expected number of further points within a distance s of an arbitrary point, divided by the overall density of the points. In practice an edge-correction is required to avoid biasing the estimation due to non-recording of points outside the polygon.
The newstyle argument and khat object were introduced in collaboration with Thomas de Cornulier to permit the mapping of counts or khats for chosen distance values, as in http://pbil.univ-lyon1.fr/R/pdf/Thema81.pdf, p.18.
See also
References
Ripley, B.D. 1976 The second-order analysis of stationary point processes, J. Appl. Prob, 13 255-266; Rowlingson, B. and Diggle, P. 1993 Splancs: spatial point pattern analysis code in S-Plus. Computers and Geosciences, 19, 627-655; the original sources can be accessed at: https://www.maths.lancs.ac.uk/~rowlings/Splancs/. See also Bivand, R. and Gebhardt, A. 2000 Implementing functions for spatial statistical analysis using the R language. Journal of Geographical Systems, 2, 307-317.
Examples
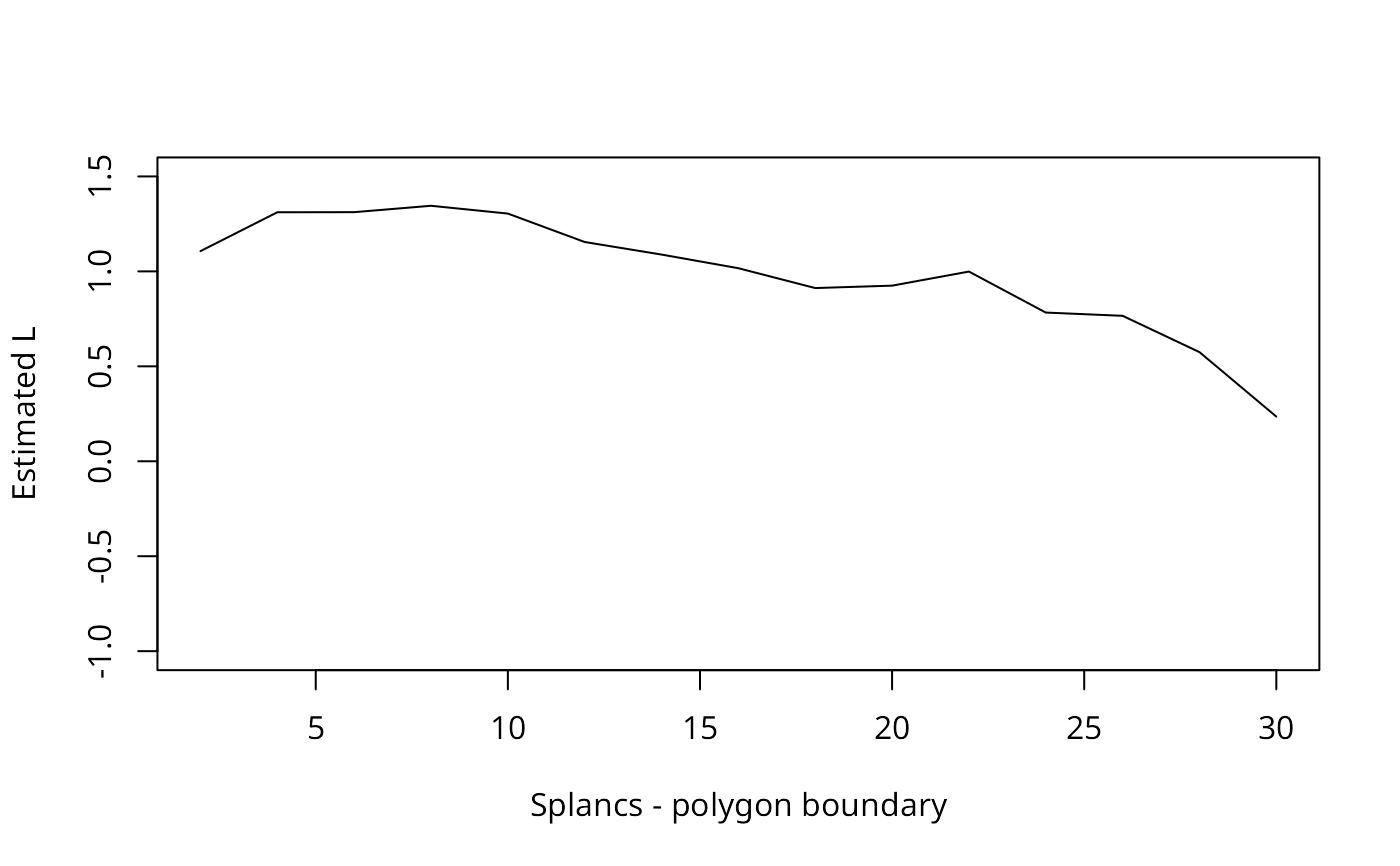
data(cardiff)
s <- seq(2,30,2)
plot(s, sqrt(khat(as.points(cardiff), cardiff$poly, s)/pi) - s,
type="l", xlab="Splancs - polygon boundary", ylab="Estimated L",
ylim=c(-1,1.5))
 newstyle <- khat(as.points(cardiff), cardiff$poly, s, newstyle=TRUE)
str(newstyle)
#> List of 4
#> $ khat : num [1:15] 30.3 88.6 168 274.4 401.5 ...
#> $ counts: int [1:168, 1:15] 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 1 2 0 ...
#> $ khats : num [1:168, 1:15] 0 0 0.22 0.441 0.22 ...
#> $ s : num [1:15] 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 ...
#> - attr(*, "class")= chr "khat"
newstyle
#> [1] 30.31848 88.62523 167.95850 274.37766 401.46106 543.63622
#> [7] 715.22877 909.69473 1123.65207 1375.54225 1661.75200 1929.58087
#> [13] 2250.68876 2565.17067 2871.96159
apply(newstyle$khats, 2, sum)
#> [1] 30.31848 88.62523 167.95850 274.37766 401.46106 543.63622
#> [7] 715.22877 909.69473 1123.65207 1375.54225 1661.75200 1929.58087
#> [13] 2250.68876 2565.17067 2871.96159
plot(newstyle)
newstyle <- khat(as.points(cardiff), cardiff$poly, s, newstyle=TRUE)
str(newstyle)
#> List of 4
#> $ khat : num [1:15] 30.3 88.6 168 274.4 401.5 ...
#> $ counts: int [1:168, 1:15] 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 1 2 0 ...
#> $ khats : num [1:168, 1:15] 0 0 0.22 0.441 0.22 ...
#> $ s : num [1:15] 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 ...
#> - attr(*, "class")= chr "khat"
newstyle
#> [1] 30.31848 88.62523 167.95850 274.37766 401.46106 543.63622
#> [7] 715.22877 909.69473 1123.65207 1375.54225 1661.75200 1929.58087
#> [13] 2250.68876 2565.17067 2871.96159
apply(newstyle$khats, 2, sum)
#> [1] 30.31848 88.62523 167.95850 274.37766 401.46106 543.63622
#> [7] 715.22877 909.69473 1123.65207 1375.54225 1661.75200 1929.58087
#> [13] 2250.68876 2565.17067 2871.96159
plot(newstyle)