Calculate simulation envelope for a Poisson Cluster Process
Kenv.pcp.RdThis function computes the envelope of Khat from simulations of a Poisson Cluster Process for a given polygon
Kenv.pcp(rho, m, s2, region.poly, larger.region=NULL, nsim, r, vectorise.loop=TRUE)Arguments
- rho
intensity of the parent process
- m
average number of offsprings per parent
- s2
variance of location of offsprings relative to their parent
- region.poly
a polygon defining the region in which the process is to be generated
- larger.region
a rectangle containing the region of interest given in the form (xl,xu,yl,yu), defaults to
sbox()around region.poly- nsim
number of simulations required
- r
vector of distances at which the K function has to be estimated
- vectorise.loop
if TRUE, use new vectorised code, if FALSE, use loop as before
Value
- ave
mean of simulations
- upper
upper bound of envelope
- lower
lower bound of envelope
References
Diggle, P. J. (1983) Statistical analysis of spatial point patterns, London: Academic Press, pp. 55-57 and 78-81; Bailey, T. C. and Gatrell, A. C. (1995) Interactive spatial data analysis, Harlow: Longman, pp. 106-109.
Examples
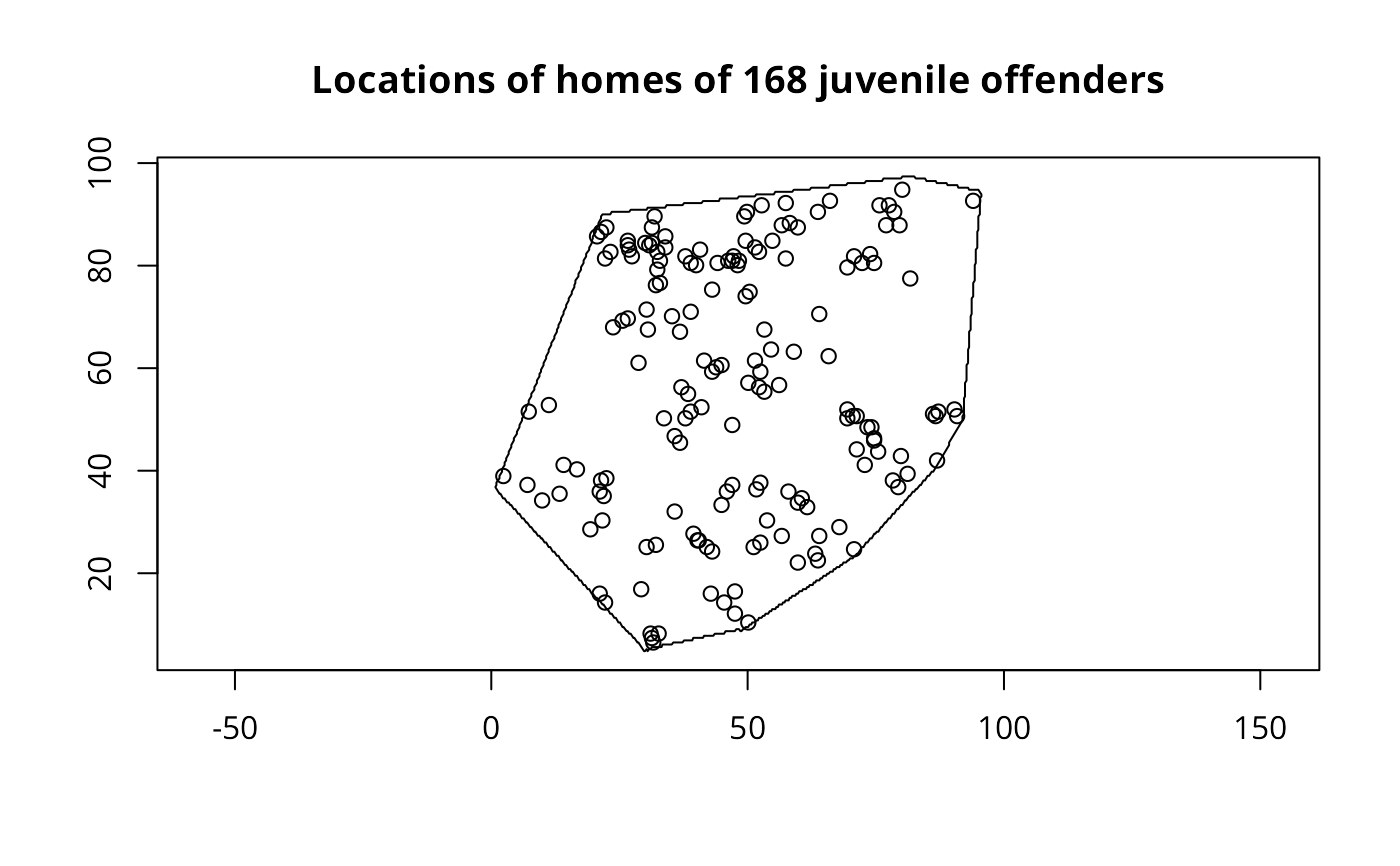
data(cardiff)
polymap(cardiff$poly)
pointmap(as.points(cardiff), add=TRUE)
title("Locations of homes of 168 juvenile offenders")
 pcp.fit <- pcp(as.points(cardiff), cardiff$poly, h0=30, n.int=30)
pcp.fit
#> $par
#> s2 rho
#> 6.16109743 0.01136752
#>
#> $value
#> [1] 0.02734823
#>
#> $counts
#> function gradient
#> 77 NA
#>
#> $convergence
#> [1] 0
#>
#> $message
#> NULL
#>
m <- npts(as.points(cardiff))/(areapl(cardiff$poly)*pcp.fit$par[2])
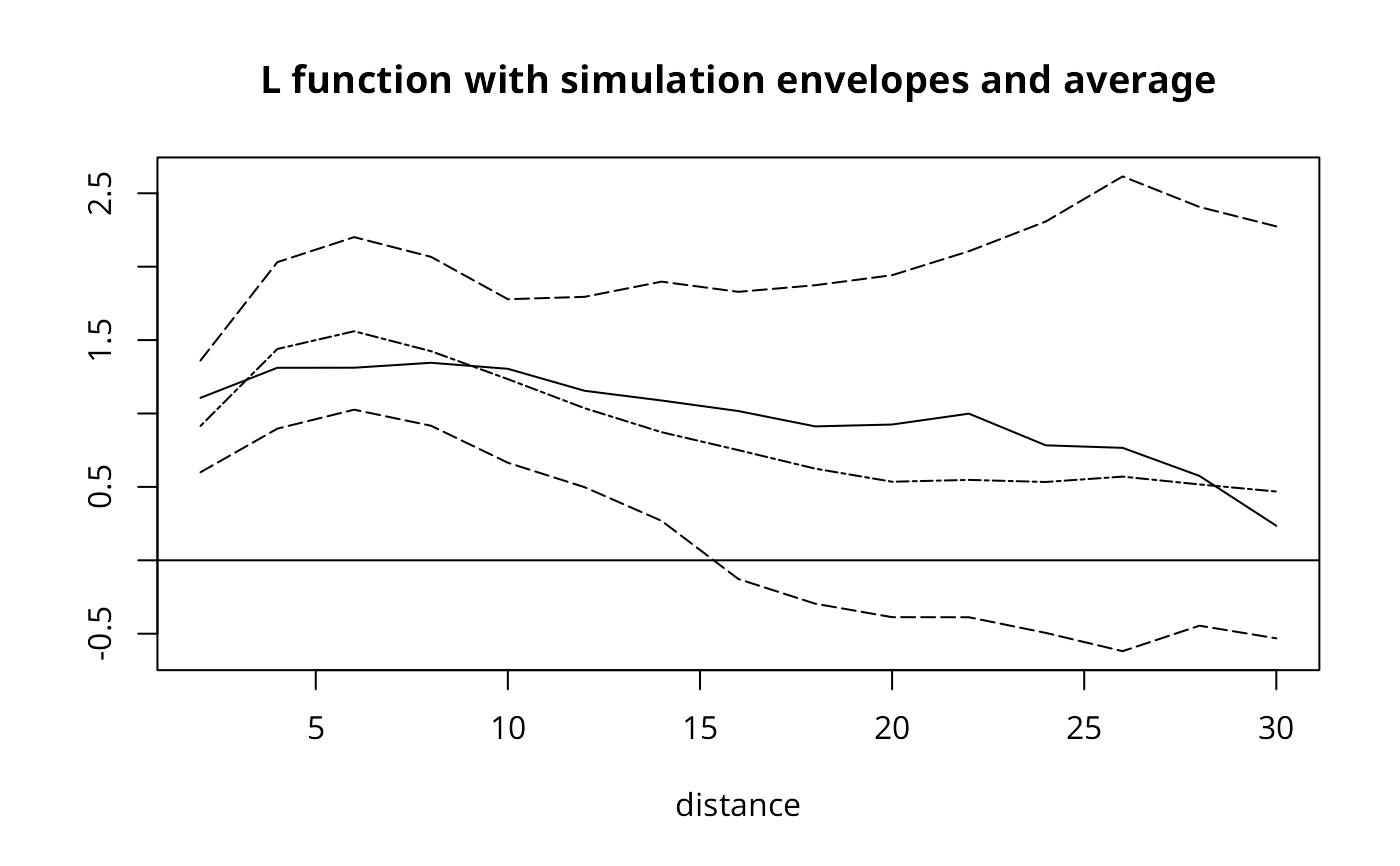
r <- seq(2,30,by=2)
K.env <- Kenv.pcp(pcp.fit$par[2], m, pcp.fit$par[1], cardiff$poly,
nsim=20, r=r)
L.env <- lapply(K.env, FUN=function(x) sqrt(x/pi)-r)
limits <- range(unlist(L.env))
plot(r, sqrt(khat(as.points(cardiff),cardiff$poly,r)/pi)-r, ylim=limits,
main="L function with simulation envelopes and average", type="l",
xlab="distance", ylab="")
lines(r, L.env$lower, lty=5)
lines(r, L.env$upper, lty=5)
lines(r, L.env$ave, lty=6)
abline(h=0)
pcp.fit <- pcp(as.points(cardiff), cardiff$poly, h0=30, n.int=30)
pcp.fit
#> $par
#> s2 rho
#> 6.16109743 0.01136752
#>
#> $value
#> [1] 0.02734823
#>
#> $counts
#> function gradient
#> 77 NA
#>
#> $convergence
#> [1] 0
#>
#> $message
#> NULL
#>
m <- npts(as.points(cardiff))/(areapl(cardiff$poly)*pcp.fit$par[2])
r <- seq(2,30,by=2)
K.env <- Kenv.pcp(pcp.fit$par[2], m, pcp.fit$par[1], cardiff$poly,
nsim=20, r=r)
L.env <- lapply(K.env, FUN=function(x) sqrt(x/pi)-r)
limits <- range(unlist(L.env))
plot(r, sqrt(khat(as.points(cardiff),cardiff$poly,r)/pi)-r, ylim=limits,
main="L function with simulation envelopes and average", type="l",
xlab="distance", ylab="")
lines(r, L.env$lower, lty=5)
lines(r, L.env$upper, lty=5)
lines(r, L.env$ave, lty=6)
abline(h=0)